Web Apps and Native Apps: Which is Best for Your Business?
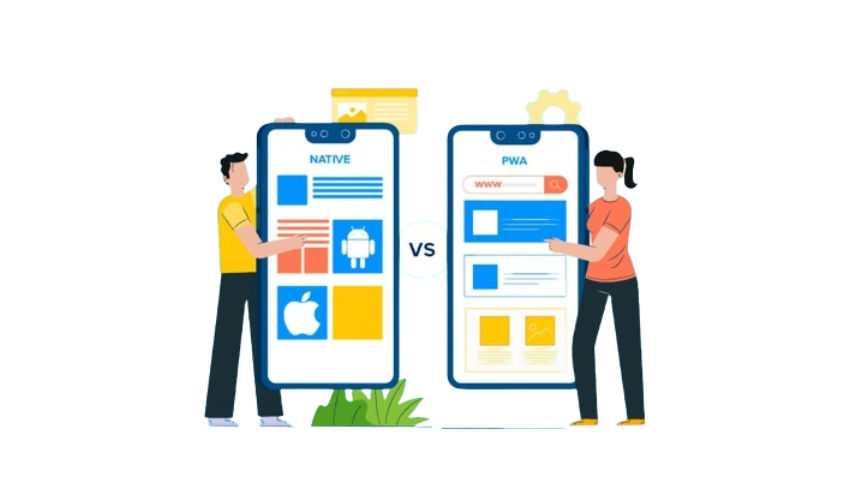

In the digital age, choosing the right type of application for your business can significantly impact your success. Two primary options are available: web apps and native apps. Each has its unique advantages and drawbacks, making it crucial to understand their differences to make an informed decision. This article will explore these differences, helping you decide which is the best fit for your business.
What is a Web App?
Web apps are applications that run on a web server, accessible through web browsers. They do not require installation on a user's device, making them highly accessible. Examples include Google Docs, Slack, and Trello. Web apps are developed using languages such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
Advantages of Web Apps
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Web apps can be accessed from any device with an internet connection and a web browser, offering greater flexibility.
- Ease of Updates: Since web apps run on a server, updates are instantly available to all users without the need for manual downloads.
- Lower Development Costs: Developing a single web app that works across multiple platforms can be more cost-effective than creating separate native apps for each operating system.
Disadvantages of Web Apps
- Performance: Web apps may not perform as well as native apps, especially with intensive tasks or complex graphics.
- Offline Functionality: Web apps typically require an internet connection to function, which can limit their usability.
- Limited Access to Device Features: Web apps often have restricted access to a device's hardware and system capabilities compared to native apps.
What is a Native App?
Native apps are applications developed specifically for a particular operating system, such as iOS or Android. They are downloaded and installed directly on a user's device from app stores like Google Play or the Apple App Store. Native apps are built using platform-specific languages like Swift for iOS and Kotlin or Java for Android.
Advantages of Native Apps
- Superior Performance: Native apps are optimized for the specific operating system, offering better performance and responsiveness.
- Full Access to Device Features: Native apps can utilize all the functionalities of a device, including the camera, GPS, and push notifications.
- Offline Functionality: Many native apps can function without an internet connection, providing a more reliable user experience.
Disadvantages of Native Apps
- Higher Development Costs: Creating separate apps for different platforms can be time-consuming and costly.
- Maintenance: Regular updates must be made to ensure compatibility with the latest operating system versions and to fix bugs, which can be resource-intensive.
- Installation Required: Users need to download and install the app, which can be a barrier to initial engagement.
Choosing the Right Option for Your Business
The decision between web apps and native apps should be based on your business goals, target audience, and resource availability.
-
Consider Web Apps If:
- You need a cost-effective solution.
- Cross-platform compatibility is a priority.
- Your application requires frequent updates.
-
Consider Native Apps If:
- Performance is crucial for your application.
- You need access to device-specific features.
- Offline functionality is essential.
Conclusion
Both web apps and native apps have their place in the business landscape. By understanding their strengths and limitations, you can choose the best option to meet your business needs. At Qono Tech, we specialize in developing both web and native apps tailored to your specific requirements. Contact us today to find out how we can help bring your vision to life.
Latest Trending
Categories
- Airbnb
- Airbnb clone
- Airbnb clone script
- Multi Vendor Marketplace Script
- Buy Sell Marketplace
- Vacation Rental Website
- Online Food Ordering and Delivery Clones
- Multi-Vendor E-Commerce Script
- Online Rental Script
- Fancy Clone
- Car Rental ScriptSoftware Development
- Car Rental Script
Never Miss Another Post!
Get updates & Valuable tips straight into your inbox once a week.